What Is Decentralization?: A Simple Beginner’s Guide To Web3
Decentralization has undoubtedly become a media buzzword. However, the principle of decentralization has the potential to be a true disruptor and create a more level playing field. In this article, we are breaking down what Web3 decentralization means and how it is being implemented.
The Basics: What does decentralization Mean In Web3?
You’re probably asking: so what is decentralization? Decentralization, specifically web3 decentralization, refers to a scenario in which power, control, and security are transferred from one central authority to several actors who jointly manage the system of interest. In this sense, decentralized systems are more resilient than their centralized counterparts, because there is no single point of failure or attack that could bring down the entire system.
However, this resilience comes at the expense of efficiency. Decentralization often results in slower transaction speeds or higher costs for users, as opposed to centralized systems where only one organization bears these costs.
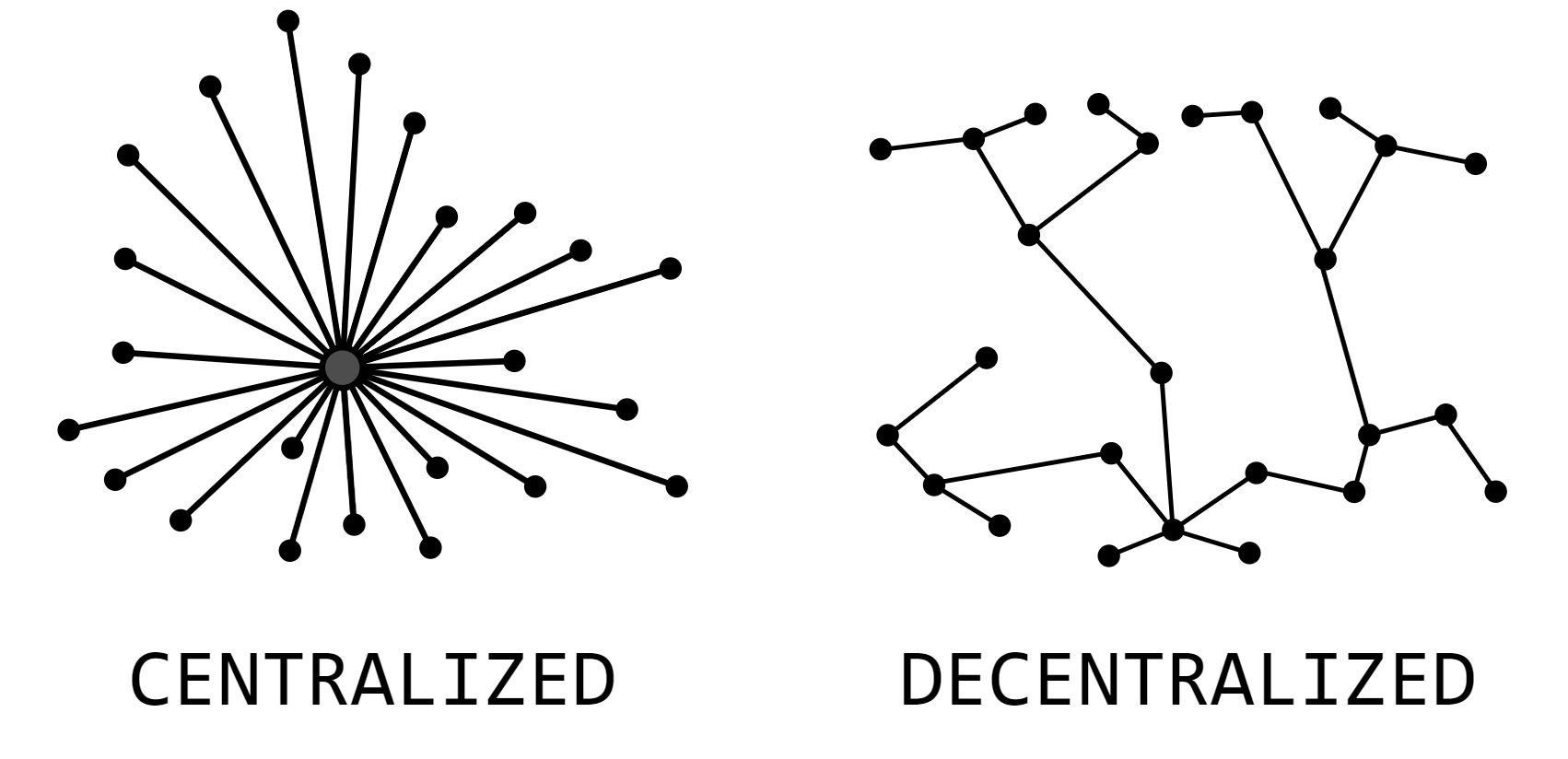
Centralization vs Decentralization
In the world of web3, decentralization is all about security and immutability. It is a way to make things more secure, and that is why it is so widely used in blockchain technology right now.
In centralized systems, there are single failure points that can be attacked or hacked by people with malicious intentions. This means that they can be controlled by governments or companies that want to use them for their own purposes. Without a doubt, this is not good for users because these entities have no incentive to protect user information from hackers or thieves. In fact, most centralized systems have been compromised multiple times over their lifetimes!
In a decentralized system, users do not rely on a single service to store their data. Instead, every user has their own copy of the database and uses it to validate transactions.
A good example of this is blockchain technology. In Ethereum, every node stores its own copy of the blockchain, allowing blockchain users to check whether they agree with any given transaction or not. Since all nodes have access to the same information at all times, there is no central point of failure where hackers could compromise security by infiltrating a server.
Additionally, decentralized systems are better at scaling, since there are more than one server handling requests. Each node can handle some portion of those requests, so the pressure is well distributed.

Practical application: Decentralized Finance
DeFi has been described as Open Finance, Web 3.0, and Big Finance 2.0, but it is really just a new way to reimagine how we do things today with blockchain technology. DeFi is essentially the decentralized version of financial services. It uses smart contracts on the blockchain to create open-source financial tools that are accessible to anyone in the world, even if they do not have access to traditional banking systems.
DeFi does not only make use of blockchain technology—but it also focuses on Web3 decentralization. Traditional finance methods rely on large institutions that control all data and transactions. Alternatively, DeFi enables different people and organisations around the globe to get involved in a financial system. It prevents a few persons or entities from having too much control over how systems operate and levels the financial playing field.
Final notes
We are all aware that the current web is not ideal. For example, Facebook has over 2 billion users, and Meta controls most of their data. Despite being a massive corporation with significant power to influence elections and shape public discourse, they are not even accountable to the government or shareholders. This creates an imbalance of power that has led to many problems in the past decade, such as “Fake News” and political ads during elections using data against users’ will.
Web3 decentralization is far from perfect. However, it is a step in the right direction for solving problems related to abuse of power. This is because it will make companies more accountable for their actions, which should lead to better products overall. Additionally, it gives back control to the users and enables them to have a choice in terms of how their data is stored and used.