What Are NFTs? – Web3 Jargon Busting
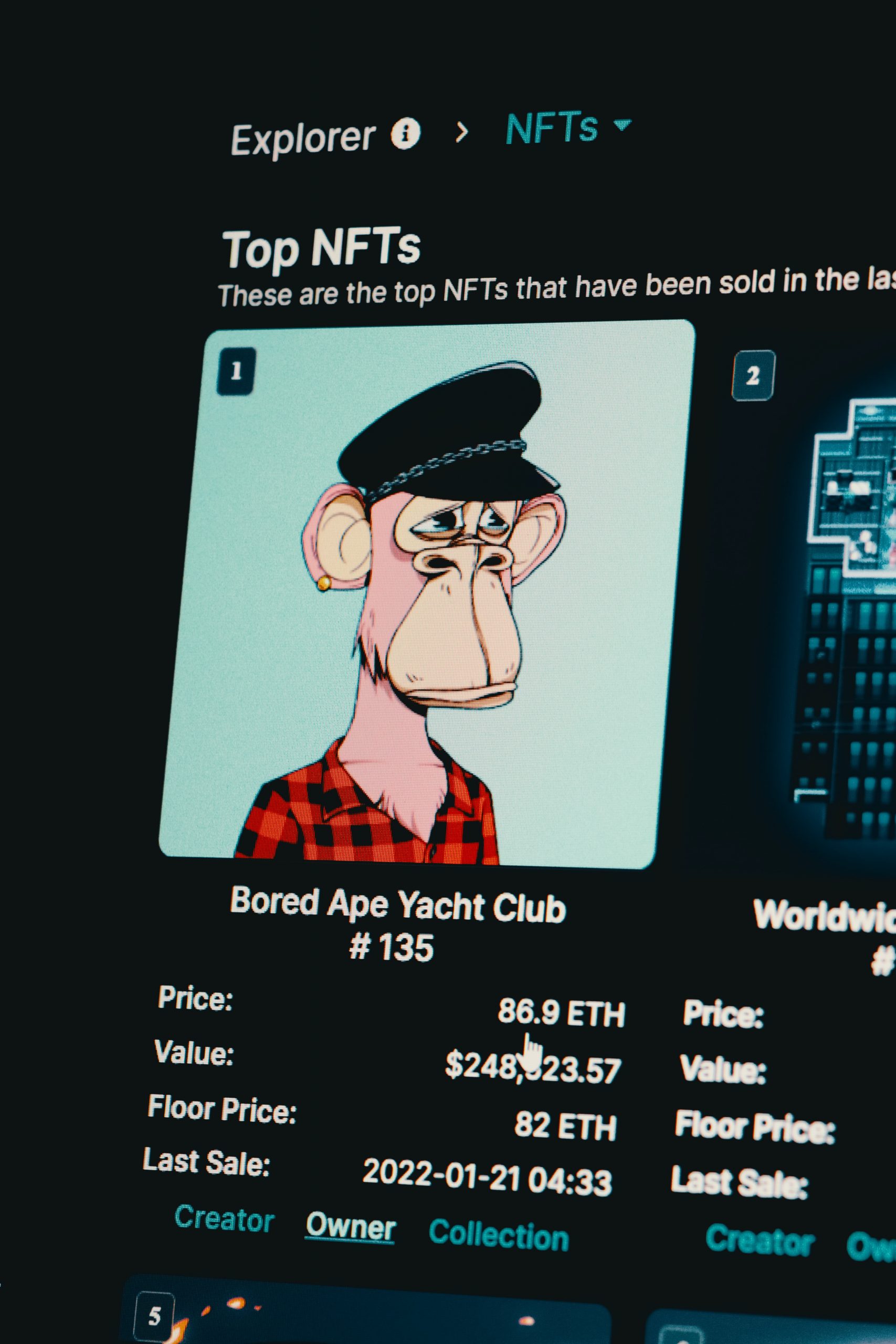
NFTs can be tricky to understand. On the most basic level, NFT stands for non-fungible token. They also represent ownership of unique, one of a kind items. This is because each non-fungible token can only have one owner at a time since its ownership is recorded on a distributed public ledger called the blockchain.

The Basics
“Fungible” refers to items that can be swapped for other things with the same value. Cash, for example, is fungible, because if we swap a 20-dollar-bill with another 20-dollar-bill, both have the same value. Cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, are also fungible.
However, many items are nonfungible. This means that they have unique qualities which determine their value. A house or a diamond necklace are two examples of nonfungible items, as no two houses or diamond necklaces are exactly the same.
NFTs are also non-fungible. This is because they are essentially digital collectibles, meaning that each token has its own unique properties. What distinguishes NFTs from other digital files is that their scarcity and authentication are stored on the blockchain; making it impossible to manipulate the data to steal ownership.
Often, NFTs are linked to physical things or access to exclusive clubs. NFT holders of specific non-fungible token collections enjoy several perks because they are NFT holders. These can range from being a member of a secret Discord server to festival VIP tickets.
As with any other new technology, NFTs are getting a lot of slack. Currently, the minting of non-fungible tokens using the proof-of-work method uses a lot of electricity. In addition, you may be scammed if you are not careful. Rug pulls occur when the creator of a non-fungible token collection abandons the project and runs away with all the money. In addition, wash trading (selling something to yourself to inflate hype and value) and money laundering are common.
However, NFTs are useful when it comes to building a community. Moreover, many non-fungible token projects have shifted their focus to utility – which means that they are bundled with several perks that are actually useful to the buyer.
Additionally, Ethereum, the backbone for the vast majority of NFTs, is switching from proof-of-work to proof-of-stake technology in the latter half of 2022. Proof-of-stake technology does not require additional energy to prove trustworthiness. As a result, the environmental impact of non-fungible tokens will be drastically reduced.
Final notes
At this point, NFTs are another way to exchange or transfer rare digital objects. In addition, there’s a big chance that NFTs will form the basis for interoperability in web3 – which means that you can use your NFTs on various blockchains, metaverses, etc. Only time will tell how NFTs will evolve.