Music Distribution: The Complete Guide
Last updated: 3 April 2024
Gone are the days when music distribution means that you have to physically deliver your album on cassette to your local record store, in the hope that the head honcho will like it enough to be distributed there. With the click of a few buttons, you can now distribute your music internationally from the comfort of your own home.
With more than 100,000 songs uploaded daily to Spotify and other DSPs, digital music distribution has become increasingly accessible. But what exactly is music distribution? And what’s the difference between music publishing and music distribution?

What is music distribution?
Music distribution is the process of making your music available to the public. In the past, physical formats such as vinyl, CD, and cassettes were the most important way to ensure that your music ended up in the hands of the public. That all changed thanks to the digital and streaming revolution.
Digital music distribution is now the fastest and cheapest way of distributing music and the primary way to reach fans and potential audiences. It’s the transmission of digital music files to DSPs that can be accessed and streamed by people on various platforms and devices.
Undoubtedly, streaming has not only changed the way artists launch their music but also radically changed the game in terms of who can access music. With streaming platforms, artists have the power to share their music with people from all over the world, with a faster turnaround than if they had to produce a physical format.
To an extent, this has levelled the playing field for independent artists, major labels, and smaller labels, as all these entities now have the capacity to release music without spending a lot of money on physical formats. This way, artists can bypass traditional gatekeepers, distribute their music themselves, release music quicker, and build a fan base through the DSPs.
So what’s the downside? While digital music distribution has opened the floodgates and enabled everyone to release music, it has dramatically increased competition. With millions of tracks available online, it’s easy to get lost. Artists must therefore ensure that they choose a distribution platform that integrates marketing tools to maximise the reach of their release and stand out from the crowd.
What are music distribution deals?
Music distribution deals are contractual agreements between an artist and a distribution company or record label that lay out the terms and conditions for releasing and distributing music. These deals enable you to put your music on DSPs, and ensure that your music is delivered and released on time.
Like any other thing in the music industry, there are various types of deals and clauses that you need to be aware of. Online distribution deals through distributors like Amplify typically charge a fixed fee for their service. This means you get 100 percent of your royalties. These types of distributors are flexible and allow for a clean break if you get signed to a record label or a bigger distribution deal.
Companies that act as label services also offer distribution deals to certain artists. Unlike online distributors, these label services companies give you access to their network and pitch your music to DSP editors. On the downside, they take anywhere between 10 and 30 percent of your royalties and likely tie you in via an exclusivity clause.
The traditional distribution deal is related to labels that almost always include a distribution deal as part of the record deal. Labels typically work with other companies that specialise in distribution, but handle things like admin, negotiations, and lobbying. In this case, both the label and the distributor claim a percentage of your royalties. Therefore, you need to read the T&Cs carefully before signing anything.

Digital music distribution versus physical music distribution: What’s the difference?
Digital music distribution and physical music distribution vary significantly. The most obvious aspect is that physical distribution involves tangible formats like vinyl, CDs, and cassettes, while digital music distribution is all digital. In the case of physical distribution, artists and their label distribute these physical formats to record stores, which then sell the records to consumers. Artists can also sell the records directly to their fans.
On the other hand, digital distribution deals with DSPs like Spotify, Apple Music, and Pandora. Artists, their labels, or a distribution company upload their music files to distributors like Amplify. These deliver the songs to DSPs, who in turn make them public on the day of release.
Undoubtedly, producing and manufacturing physical formats cost money. While costs vary, you always have to take into account things such as artwork design, printing, pressing, and packaging.
In addition, you also need space where you can store the formats, rely on postal services to deliver the records, negotiate with record stores to distribute the records, and deal with returns and damages. Digital eliminates all these headaches. While there are still costs (you have to record, mix and master the music, after all!), you eliminate all the expenses associated with releasing a physical product.
Physical distribution relies on record stores accepting X number of records and selling them. Having a physical format is undoubtedly a personal experience for both the artist and the fan, but limits the reach to specific locations and stores. Moreover, if you’re aiming for an international release, you typically need to work with different location-specific partners.
With digital distribution, you can reach people on a global scale without the need for different distribution partners. This allows you to reach a wider and more global audience quickly and cheaply.
In addition, the online nature of digital music distribution enables artists and their teams to have a look at who’s listening to the songs via audience analysis. In-depth audience analysis can be tricky when distributing physical records, as it’s harder to obtain this data.
One of the main disadvantages of digital distribution is that you earn much less per stream than per unit sold. The streaming royalties are further split between the artist, label, and distribution company. However, it’s important to remember that physical music distribution requires upfront costs, while digital distribution costs are relatively low. Therefore, there’s no denying the impact of digital music distribution on making music distribution more accessible to independent artists.
What’s the difference between music publishing and music distribution?
While music publishing and music distribution are interconnected, the former deals with rights, royalty collection and administration, and licensing, while distribution is about getting the music to stores and streaming platforms.
Music publishing focuses on the management of copyrights and the protection of copyright and intellectual property rights. This includes addressing any infringements, as well as registering songs and attributing them to the correct songwriters.
Additionally, publishers collect and administer royalties on behalf of songwriters and copyright holders, and liaise with organisations such as PROs to collect these royalties. Most publishers also deal with licensing and syncs. They pitch the songs for potential placement on films and television shows, and grant mechanical and performance licenses for public performances and all media.
On the other hand, music distributors ensure that the songs reach the public, whether through physical or digital formats. Music distributors typically handle the production, shipping, and distribution of physical formats, as well as the digital encoding and uploading of audio files to DSPs.
Distributors also have agreements with publishers and DSPs to track the revenue generated by these platforms and forward it to publishers, artists, and record labels. In this way, music distribution and music publishing overlap. It’s important to note that artists need both to successfully release their music, monetise their work, and ensure that all their rights are protected.
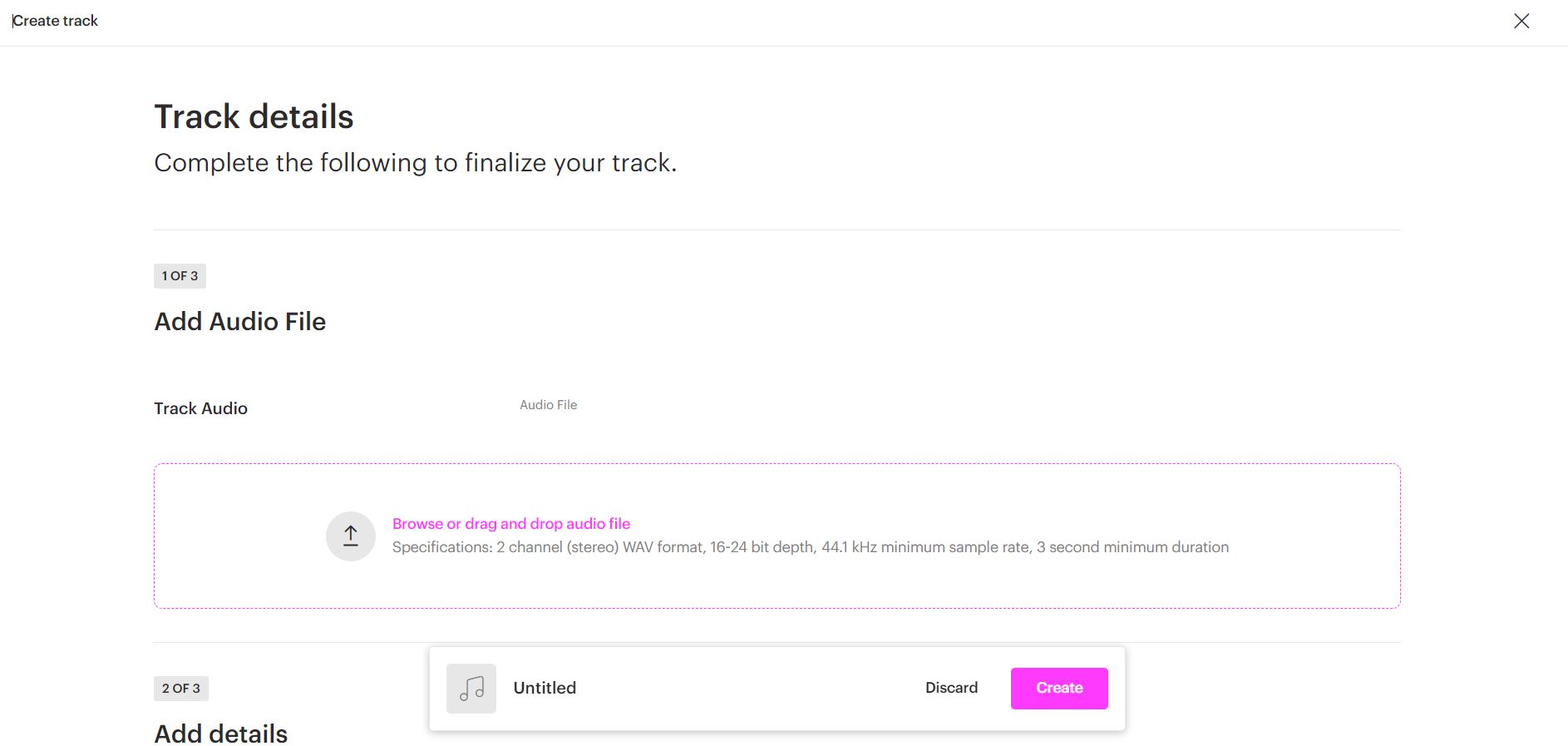
How to distribute your music using Amplify
In addition to other marketing perks, AmplifyLink Pro enables you to distribute your music through Amplify. With Amplify, you can distribute your songs to all major music platforms, and keep 100 percent of your royalties and rights. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to distribute your music using Amplify.
1 Sign up to Amplify and create your artist page
2 Click on “Distro”
3 Click on “Create Release” or “Create Track” and fill out all the information
4 Click on “Create.” Congratulations! You’ve just uploaded your first release through Amplify






